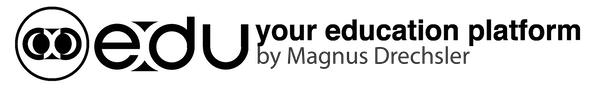Additional resources
Spectroscopic identification
Understandings● The degree of unsaturation or index of hydrogen defi ciency (IHD) can be used to determine from
a molecular formula the number of rings or multiple bonds in a molecule. ● Mass spectrometry (MS), proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H NMR), and infrared spectroscopy (IR) are techniques that can be used to help identify and to determine the structure of compounds. Guidance ● The electromagnetic spectrum (EMS) is given in the data booklet in section 3. The regions employed for each technique should be understood. ● The operating principles are not required for any of these methods. |
Applications and skills● Determination of the IHD from a molecular formula.
● Deduction of information about the structural features of a compound from percentage composition data, MS, 1H NMR, or IR. Guidance ● The data booklet contains characteristic ranges for IR absorptions (section 26), 1H NMR data (section 27), specifi c MS fragments (section 28), and the formula to determine IHD. For 1H NMR, only the ability to deduce the number of different hydrogen (proton) environments and the relative numbers of hydrogen atoms in each environment is required. Integration traces should be covered but splitting patterns are not required. |
HL Spectroscopic identification of Organic compounds
Understandings● Structural identifi cation of compounds involves several different analytical techniques, including
IR, 1H NMR, and MS. ● In a high-resolution 1H NMR spectrum, single peaks present in low resolution can split into further clusters of peaks. ● The structural technique of single crystal X-ray crystallography can be used to identify the bond lengths and bond angles of crystalline compounds. Guidance ● The operating principles are not required for any of these methods. ● High resolution 1H NMR should be covered. ● The precise details of single crystal X-ray crystallography need not be known in detail, but students should be aware of the existence of this structural technique in the wider context of structural identifi cation of both inorganic and organic compounds. |
Applications and skills● Explanation of the use of tetramethylsilane (TMS) as the reference standard.
● Deduction of the structure of a compound given information from a range of analytical characterization techniques (X-ray crystallography, IR, 1H NMR, and MS). Guidance Students should be able to interpret the following from 1H NMR spectra: number of peaks, area under each peak, chemical shift, and splitting patterns. Treatment of spin–spin coupling constants will not be assessed but students should be familiar with singlets, doublets, triplets, and quartets. |
Infrared spectroscopy
|
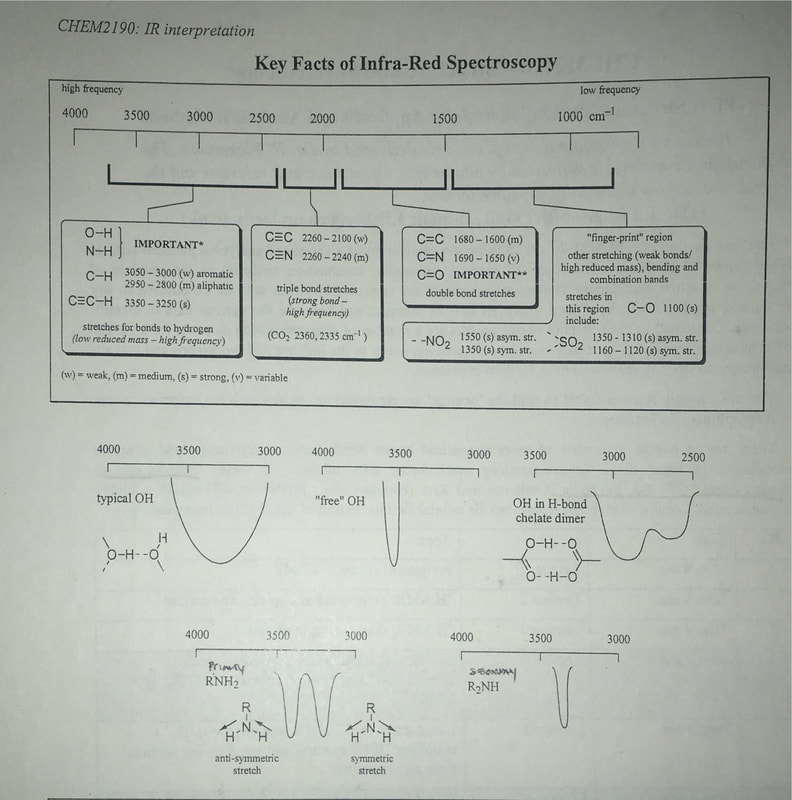
NMR spectroscopy
|
Research task - IR and NMR spectroscopy
|
Drug synthesis case studyTask:
1. Go through the slides and complete the tasks set. (use the link if the embedded slides do not load) 2. Complete a full analysis of the IR and NMR spectra of Ibuprofen and explain your analysis using flipgrid |
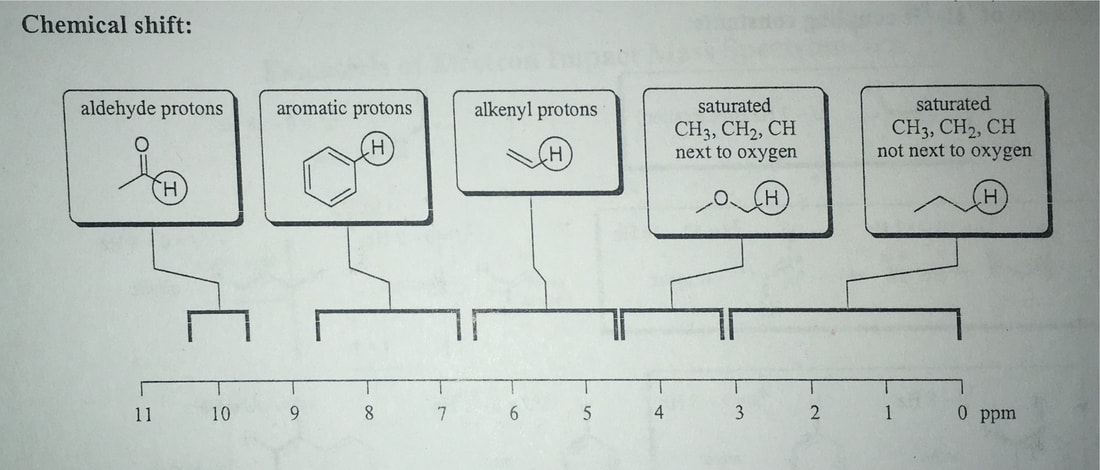
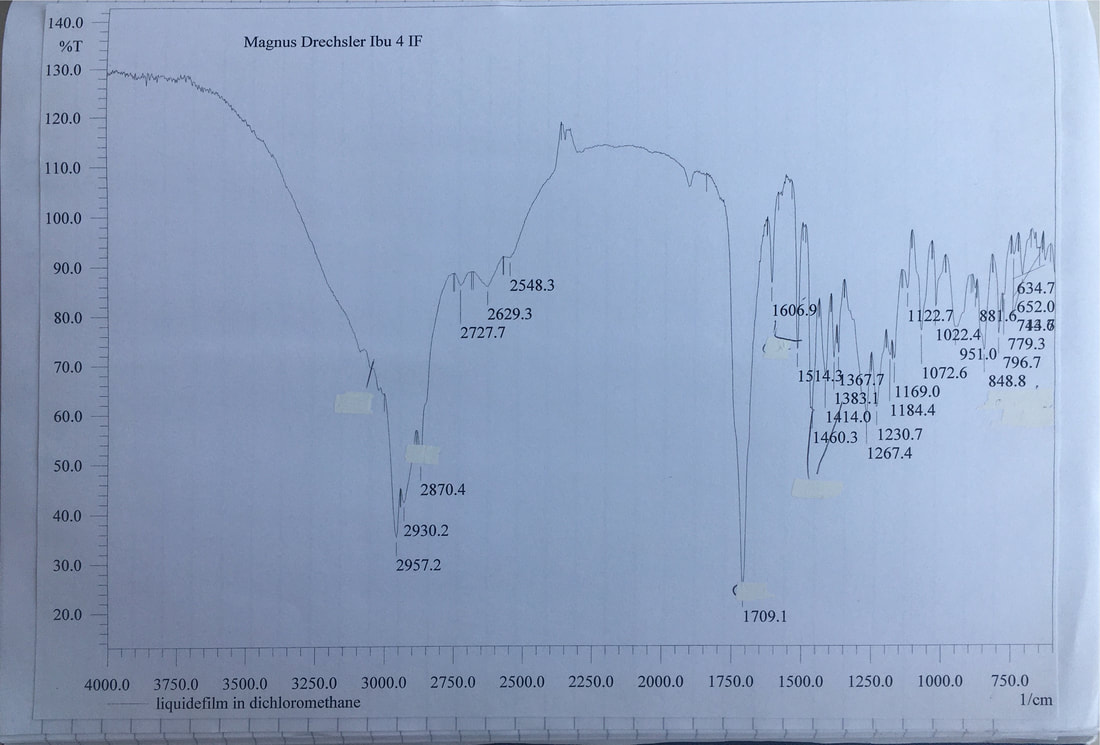
IR Spectrum of Ibuprofen
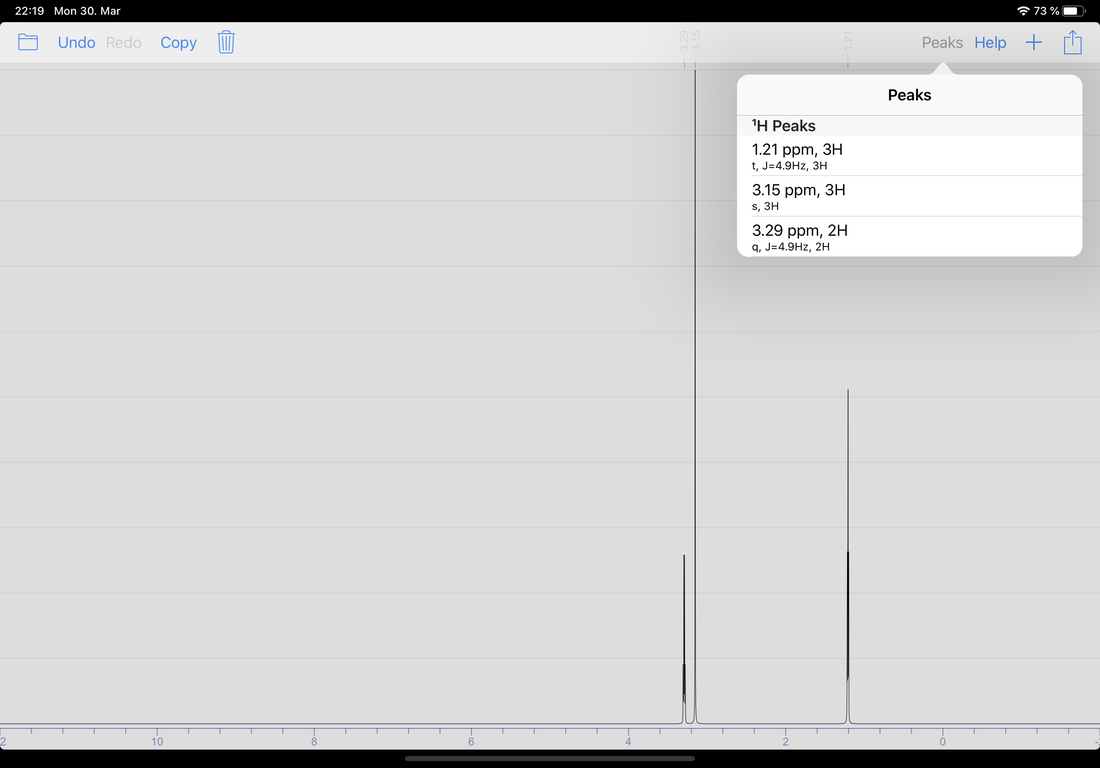
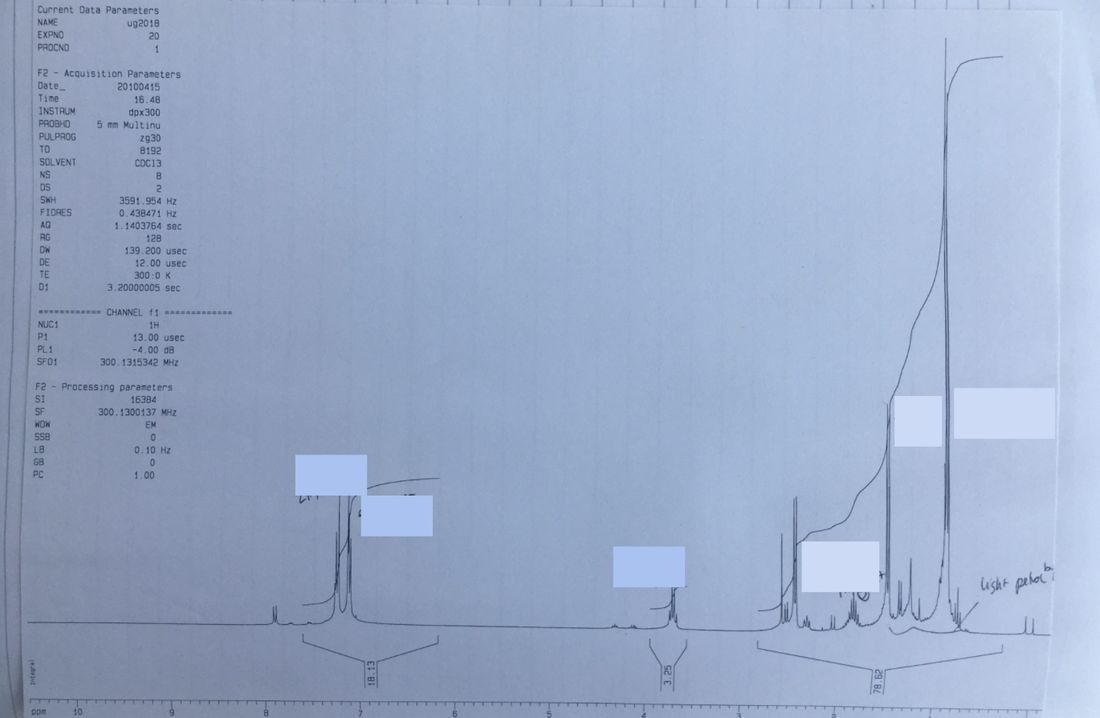
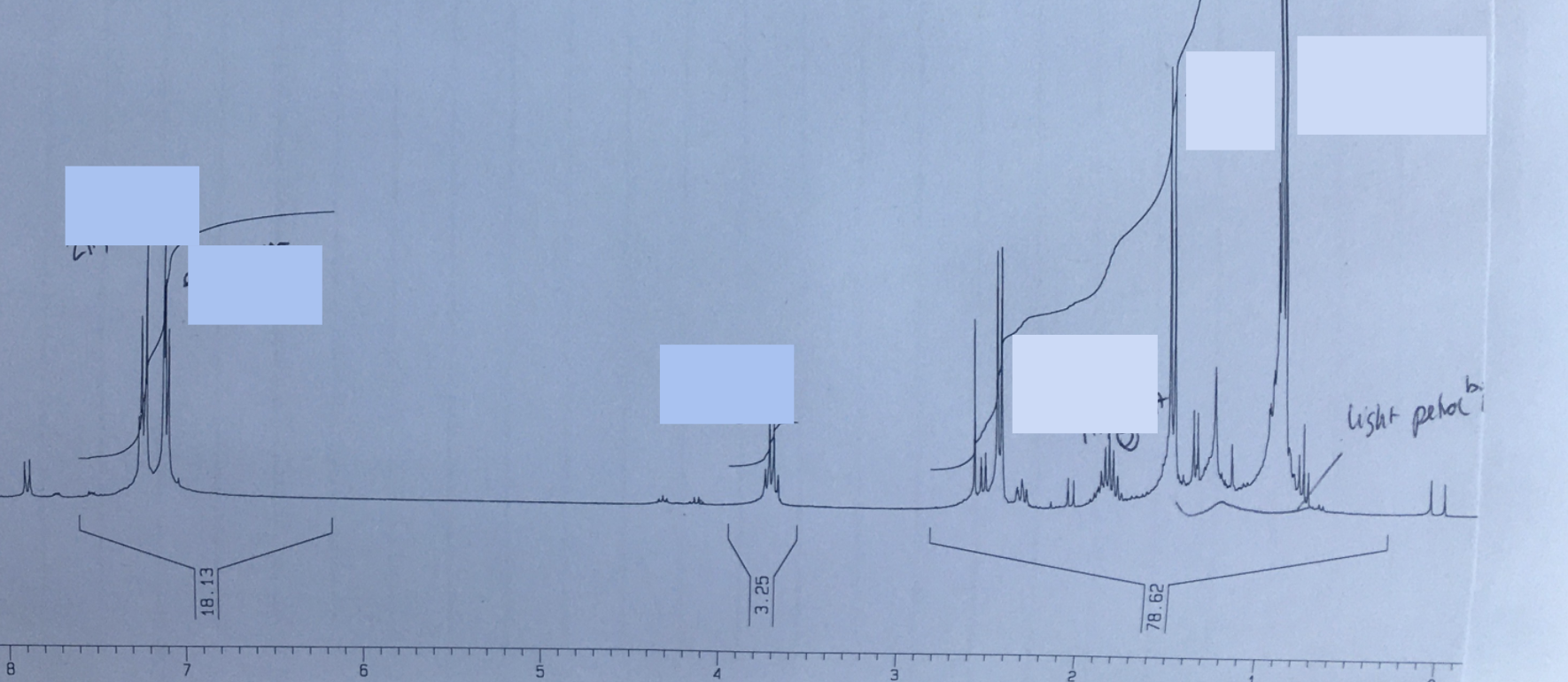
NMR spectrum of Ibuprofen
Student samples of Aspirin: Analysing IR and NMRTask:
|