|
● The characteristics of the pH curves produced by the different combinations of strong and weak
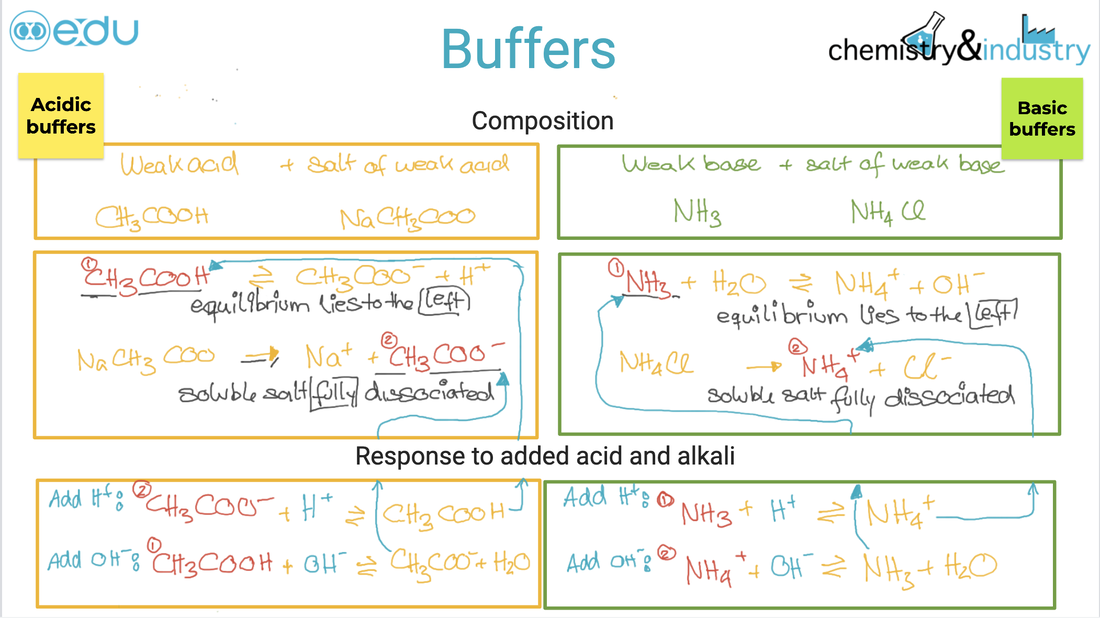
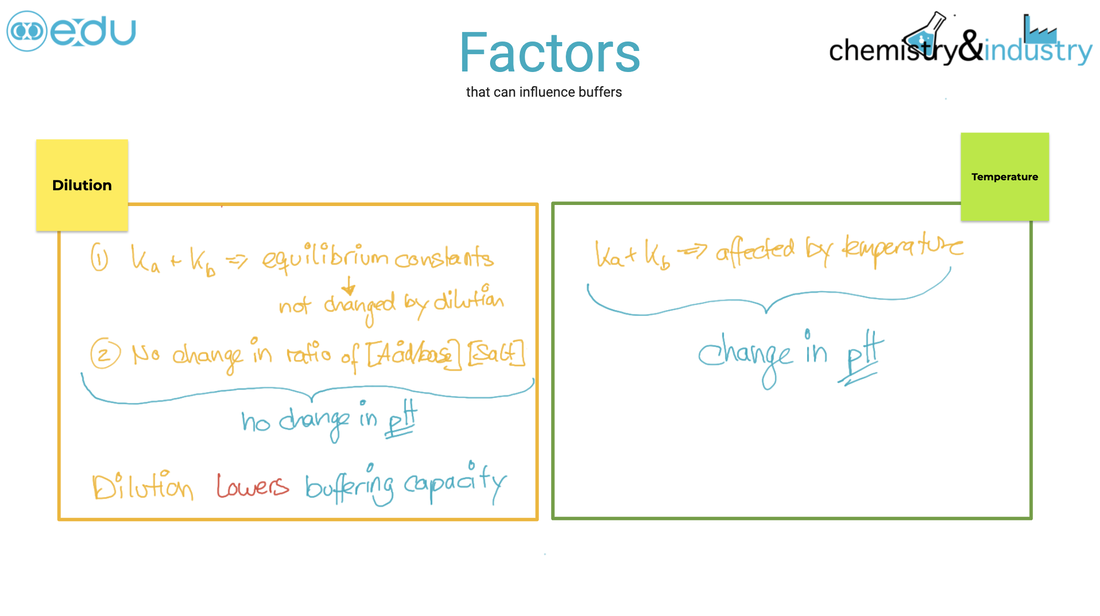
acid and bases. ● An acid–base indicator is a weak acid or a weak base where the components of the conjugate acid–base pair have different colours. Guidance ● For an indicator which is a weak acid: HIn(aq) s H+(aq) + In–(aq) ● For an indicator which is a weak base: BOH(aq) s B+(aq) + OH–(aq) ● Examples of indicators are listed in the data booklet in section 22. ● The relationship between the pH range of an acid–base indicator, which is a weak acid, and its pKa value. Guidance The colour change can be considered to take place over a range of pKa ± 1. ● The buffer region on the pH curve represents the region where small additions of acid or base result in little or no change in pH. ● The composition and action of a buffer solution. |
● The general shapes of graphs of pH against volume for titrations involving strong and weak acids and bases with an explanation of their important features.
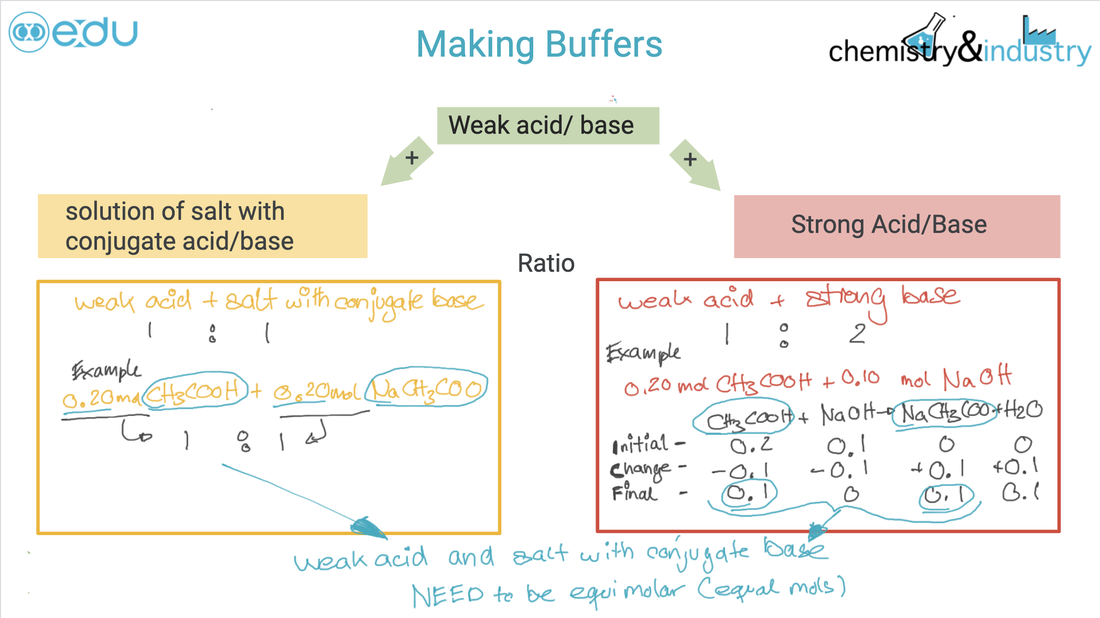
Guidance ● Only examples involving the transfer of one proton will be assessed. Important features are: intercept with pH axis equivalence point buffer region points where pKa = pH or pKb = pOH ● Selection of an appropriate indicator for a titration, given the equivalence point of the titration and the end-point of the indicator. ● While the nature of the acid–base buffer always remains the same, buffer solutions can be prepared by either mixing a weak acid/base with a solution of a salt containing its conjugate, or by partial neutralization of a weak acid/base with a strong acid/base. ● Prediction of the relative pH of aqueous salt solutions formed by the different combinations of strong and weak acid and base. Guidance ● Salts formed from the four possible combinations of strong and weak acids and bases should be considered. Calculations are not required. ● The acidity of hydrated transition metal ions is covered in topic 13. The treatment of other hydrated metal ions is not required. |
|
18.3 How do acid-base indicator change colour depending on the pH?
|
18.3 What are the characteristics of the pH curves produced by the different combinations of strong and weak acid and bases?
18.3 What is the relationship between the pH range of an acid–base indicator, which is a weak acid, and its pKa value? |
|
This video gives you some real world examples of buffers and explains how buffers work. It also revise your knowledge of equilibrium and acids and bases calculations.
Task:
|
|
|
Task:
|
|
Task:
1. Use a pH probe to investigate varies curves
- Strong acid & Strong base
- Strong Base & weak acid
- Strong acid & weak base
- Weak acid & weak base
1. Use a pH probe to investigate varies curves
- Strong acid & Strong base
- Strong Base & weak acid
- Strong acid & weak base
- Weak acid & weak base
2. Analyse the data in the folder above
- Select one of the 3 groups
- convert graphs to images or take a screenshot of them
- Create a Jamboard and add the images of the graphs
- Make notes and drawings on the graph when you analysing the graph
- Share the Jamboard with your teacher
- highlights of characteristic of each specific pH curve (annotate the graph and use drawings)
- Explanation of how accurate the pH curve is. Include your justification