|
Structure 1.1.1
|
|
Balancing equation demo
|
Please note that the equations below may be unbalanced
Synthesis: (Oxidation of Magnesium) Mg + O2 -> MgO Decomposition: (Elephant toothpaste) H2O2 -> H2O + O2 Double replacement: (Precipitation reaction) Pb(NO3)2 + KI -> PbI2 + KNO3 Combustion: (Whoosh bottle) C2H5OH + O2 -> H2O + CO2 TASK: Balance the equations above |
|
Balancing equations
|
Task:
Understand how to balance symbol equations and learn what not to do. This video takes you through the process and completes several examples to deepen your understanding. Ensure that you are work through the examples in video on your own as you watch. |
|
Atom economy
|
This video explains atom economy using organic substances by working through set problems.
Ensure that you work through the problems on your own as you watch the video and pause the video when it asks you to do so. |
|
Task1:
- Watch the videos
- Take notes of the reactions and balanced equations
- Find images of reactions, as well as the balanced equation
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Task:
1. Complete the introduction and balance all 3 reactions
2. Play a game
1. Complete the introduction and balance all 3 reactions
2. Play a game
Quiz time:
- Complete all the question in the quiz
- Self assess your answers by checking after raking the quiz which answer you have answered incorrectly
- If you have answered some questions incorrectly., seek advice from your classmates to solve the problem
Energy changes between states of matter
|
|
This video is reminding you of the states of matter and the energy changes involved in the state changes. It also explains what states substances are at room temperature and why, which is key to identify states symbols for reactants and products in symbol equations.
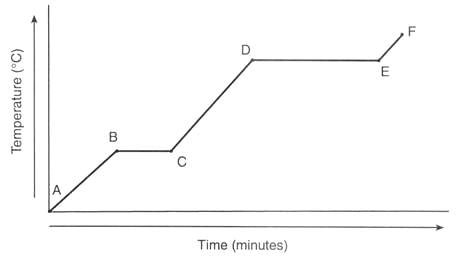
TASK 1: Identify the state symbols in the following equations: CH4 + 2O2 -> CO2 + 2H2O (remember here that this is a combustion equation and the CO2 and H2O are not at room temperature) TASK 2: Explain what is happening during the following parts of the graph. Ensure that you use the concept of kinetic energy and breaking of inter-particle forces in your explanation. 1) From A to B 2) From B to C 3) From C to D 4) From D to E 5) From E to F Answer: You can find the answer in the Pearson DP Chemistry text book on page 13
Blog task:
Click on the Blog button below and write a comment about the difference between boiling and evaporation. If you are unsure , please watch the video again. In addition, read at least one of your classmates comments and respond to your classmate what he or she explained well and what he or she could explain better. |
homogenous and heterogenous mixtures
|
only needed to watch until 3:50min.
|
This video discusses the different types of homogenous and heterogenous mixtures.
Task:
Take notes in the diagram of all the different types of mixtures |
This video is linking to the theme of Unit 3 which is all about cooking.