Understandings● Positive ions (cations) form by metals losing valence electrons.
● Negative ions (anions) form by non-metals gaining electrons. ● The number of electrons lost or gained is determined by the electron configuration of the atom. ● The ionic bond is due to electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions. ● Under normal conditions, ionic compounds are usually solids with lattice structures. |
Applications and skills● Deduction of the formula and name of an ionic compound from its component ions, including
polyatomic ions. Guidance Students should be familiar with the names of these polyatomic ions: NH4+, OH–, NO3–, HCO3–, CO32–, SO42–, and PO43– ● Explanation of the physical properties of ionic compounds (volatility, electrical conductivity, and solubility) in terms of their structure. |
Additional Resources
|
Chemical bonding overview videos
Check out the video and learn from your peers
Want to add your video?
Use this access code - chemsitry8materials
Want to add your video?
Use this access code - chemsitry8materials
Exploration tasks
|
1) Describe how the ionic bond is due to electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions.
|
2) Explain the physical properties of ionic compounds (volatility, electrical conductivity, and
solubility) in terms of their structure. |
3) Describe how a covalent bond is formed by the electrostatic attraction between a shared pair of electrons and
the positively charged nuclei. |
|
8) Explain electrical conductivity and malleability in metals.
|
Bonding |
4) Deduce the polar nature of a covalent bond from electronegativity values.
|
|
7) Describe how a metallic bond is the electrostatic attraction between a lattice of positive ions and delocalized
electrons. |
6) Deduce the types of intermolecular force present in substances, based on their structure and
chemical formula. |
5) Use of VSEPR theory to predict the electron domain geometry and the molecular geometry for
species with two, three, and four electron domains. |
Exploration resources for each task
|
Task 1:
|
|
Task 2:
|
|
Task 3:
|
|
Task 4:
|
|
Task 5:
|
|
Task 6:
|
|
Task 7:
|
|
Task 8:
|
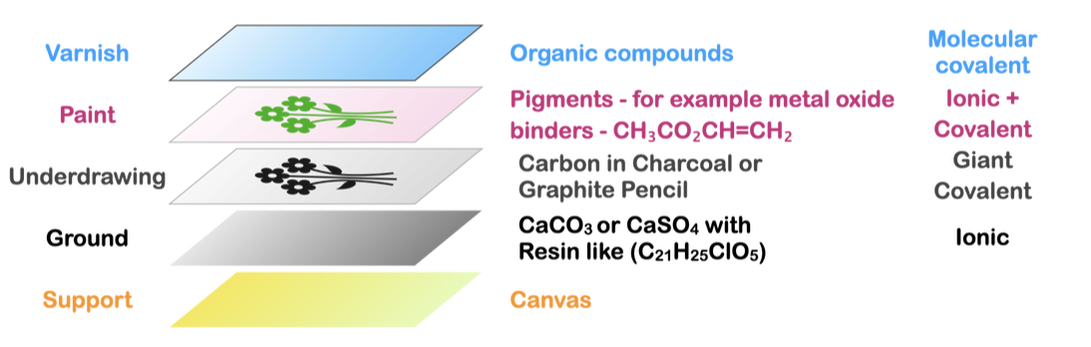
Materials in the layers of an Easel PaintingThis video outlines the materials that are present in each of the layers of an easel painting.
Task :
|
Innovation: Demonstrating understanding on chemical bonding in innovative ways
Examples of Songs
Role play (even with animals)
|
Student Practical: Growing your own crystal - ionic bonding
|
Task:
|
|
Polyatomic ions quiz - Kahoot |
Ionic bonding and ionic compounds
|
Physical properties of ionic compounds that reflect the lattice structureTask:
|