Understandings● A covalent bond is formed by the electrostatic attraction between a shared pair of electrons and
the positively charged nuclei. ● Single, double, and triple covalent bonds involve one, two, and three shared pairs of electrons respectively. ● Bond length decreases and bond strength increases as the number of shared electrons increases. ● Bond polarity results from the difference in electronegativities of the bonded atoms. Guidance Bond polarity can be shown either with partial charges, dipoles, or vectors. |
Applications and skills● Deduction of the polar nature of a covalent bond from electronegativity values.
Guidance Electronegativity values are given in section 8 of the data booklet. |
Lewis dot structure/ Dot and Cross Diagram
|
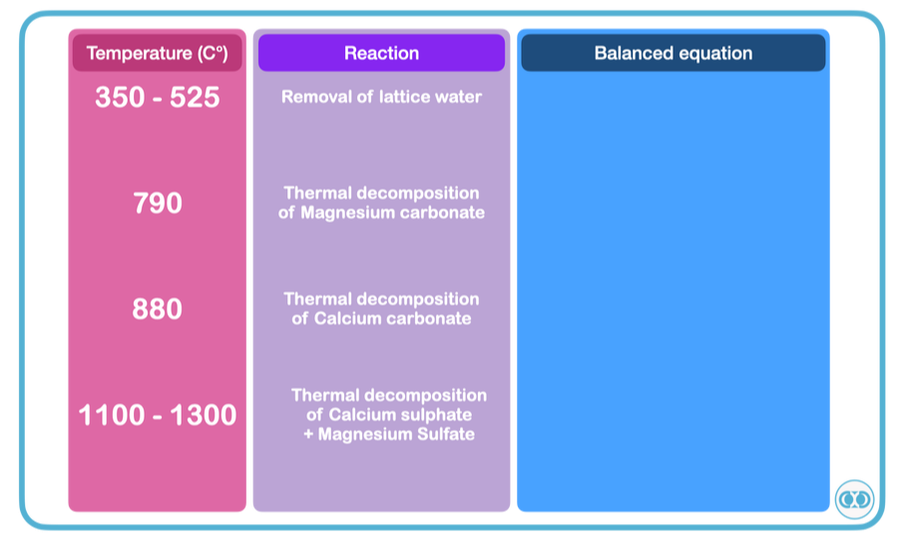
Collaboration with DP Visual Art: Student knowledge and skills exchangeFiring process of clay:
The video is describing the baking of clay in a Kiln and outlining the reactions that take place during the firing process. Reactions that take place during the firing process:
Pottery glazes:
This video is describing the colours of glazes before and after the firing process. Chemical reaction equations are used to understand an y colour changes. Preparation for student knowledge/skills exchange:
DP Chemistry students:
DP Visual Art students:
Extra resources:
|
Polarity
|
Covalent bonding and intermolecular forces Kahoot |