Understandings● Emission spectra are produced when photons are emitted from atoms as excited electrons return
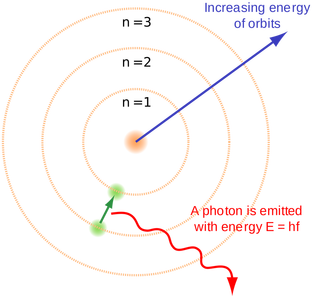
to a lower energy level. ● The line emission spectrum of hydrogen provides evidence for the existence of electrons in discrete energy levels, which converge at higher energies. Guidance The names of the different series in the hydrogen line spectrum are not required. ● The main energy level or shell is given an integer number, n, and can hold a maximum number of electrons, 2n2. ● A more detailed model of the atom describes the division of the main energy level into s, p, d, and f sub-levels of successively higher energies. ● Sub-levels contain a fi xed number of orbitals, regions of space where there is a high probability of fi nding an electron. ● Each orbital has a defi ned energy state for a given electronic confi guration and chemical environment and can hold two electrons of opposite spin. |
Applications and skillsDescription of the relationship between colour, wavelength, frequency, and energy across the
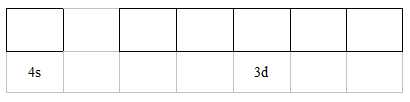
electromagnetic spectrum. Guidance Details of the electromagnetic spectrum are given in the IB data booklet in section 3. ● Distinction between a continuous spectrum and a line spectrum. ● Description of the emission spectrum of the hydrogen atom, including the relationships between the lines and energy transitions to the fi rst, second, and third energy levels. ● Recognition of the shape of an s orbital and the px, py, and pz atomic orbitals. ● Application of the Aufbau principle, Hund’s rule, and the Pauli exclusion principle to write electron confi gurations for atoms and ions up to Z = 36. Guidance ● Full electron confi gurations (e.g. 1s22s22p63s23p4) and condensed electron confi gurations (e.g. [Ne]3s23p4) should be covered. ● Orbital diagrams should be used to represent the character and relative energy of orbitals. The electron confi gurations of Cr and Cu as exceptions should be covered. |
Inquiry Questions |
Electromagnetic spectrum intro
2.2 Electron configuration
|
The video "Energy levels - AS Quantum" explains about the energy levels in atoms. It explains how photons can transition electrons from the ground state to the an excited state. In addition, the video illustrates what happens when the excited electrons transitions back to the ground state.
|
|
|
Question: Energy levels and emission spectrum
Look at the picture of the hydrogen line emission spectrum (figure 1) below and discuss why this emission spectra has only certain lines rather than the whole spectra with all the colours. Use the video "Energy levels - AS Quantum" and figure 2 to help you explain using scientific reasoning. |
Demo: Properties of light and the application in ArtThe video shows how from white light (sunlight) one generates all of the colours of the materials that the artist is using. Those materials cause the transformation of white light to the colours that the artist want to portray.
Task:
|
|
|
|
Test your understanding and skills Ch 2 + 12 |